Lesson 2
Prior Knowledge
Students should already know:
- the metalanguage used to analyse visual images
Lesson Objectives
Students will be able to
-
Analyse and explain using the appropriate metalanguage to discuss how the features of Print Advertisement are influenced by the interests of the producer.
-
Construct a rubric using engagement strategies to guide the design process and the assessment of Print Advertisement artefacts.
materials
Transmedia Story: Coraline
-Writing materials and paper
- Personal Learning Devices/ Ipads
- Google Document (One for each group)
resources
- Appendix 1: Metalanguage
- Video Resource: From 00:00- 1:07mins
- Appendix 4: Examples of Multimodal & Transmedia Texts
- Appendix 5: Coraline Movie Poster
- Appendix 6: Analysis of the Visual and Langauge Features
- Appendix 7: Guided Practice Resources
- Appendix 8: Suggested Class Rubrics
Tune In (10mins)
Resources needed:
-
Video Resource
-
Appendix 4
description
-
Using the movie clip, teacher gets students to recall and discuss how it is a digital multimodal text and a transmedia story and what it means by a "digital multimodal text" and a "transmedia story"
-
Teacher provides other examples of multimodal texts and transmedia stories (Appendix 4).
Key Teacher Langauge
-
What are some semiotic modes present in this digital text?
-
Using examples from the text, how do the different semiotic modes work together to convey meaning?
-
What do you think transmedia means? What are some characteristics of a transmedia story?
-
What are some examples of multimodal texts that you know of and what modes are present?
rationale
Transmedia skills are a series of competences related to the digital interactive media production, sharing and consumption (Scolari, 2018). By reviewing the movie clip and the other examples in Appendix 4, it presents a set of transmedia narratives that may not be the typical story narrative that one hears (e.g. The wolf in The Three Little Pigs). They heighten the students' interactions with multimodal text beyond a passive consumption, but the sharing and production skills as well.
Further, the introduction of the alternative endings and the fanfiction will also be an apt introduction to transmedia, in which it exposes the students to the alternative narratives and the stories are all cohesive within the set of world rules. Students may become more aware of the intertextuality of transmedia texts in offering unique content for the viewers while contributing to the whole experience with the story universe (Jenkins, 2007).

Appendix 4:
Examples of Multimodal & Transmedia Texts
Fanfiction: https://archiveofourown.org/works/5096105
Lesson Development I
(40mins)
Resources needed:
-
Appendix 5
-
Appendix 6
-
Appendix 7
description
Situated Practice
Teacher shows the class the tagline "Be careful what you wish for".
Teacher will ask students to brainstorm their interpretations of this tagline and why they make such meanings from the words.
Key Teacher Language:
-
What comes to mind when you hear this phrase?
-
What do you understand by this phrase?
Modelling the Text
Teacher shows students the movie poster (Appendix 5) and guides them through the following Guiding Questions.
Guiding Questions:
-
What type of text is this? How do you know?
-
What do you see? What stands out to you the most?
-
Who do you think created this poster?
-
Why do you think the producer designed this poster?
-
Who do you think is the target consumer?
-
How has your understanding of this tagline changed?
-------------------------------------------
Overt Instruction:
Teacher introduces the design conventions and features in the text (Appendix 6). Teacher explains how the text and images work together to entice the viewer to achieve the purpose of the producer which the viewer should be able to identify when they view critically.
-------------------------------------------
Guided Practice
In their groups, the students will analyse the text features of their selected advertisement (Appendix 7) using the metalanguage and explain how they work together to achieve the purpose of the producer. Note that the purpose is provided to the students on Padlet.
Students to post their analysis on Padlet.
rationale
Situated Practice
The use of the tagline alone serves as building the context for the students in the Curriculum Cycle for Print Advertisements. Also, it connects to the previous lesson by presenting in just a single mode and asking for the the meanings made. They will experience the known (the multimodal skills and sensitivity to the presence/lack of modes) and the new (the new transmedia text).
Modelling the Text
In this stage of the Curriculum Cycle, the teacher is inductively guiding the students to be co-creators of knowledge regarding Print Advertisements. She is also demonstrating viewing skills to the students where the guiding questions also serve as the metalanguage for viewing Print Advertisements. As they provide their affective responses and engage in ideological skills, they are engaging in Critical visual literacy (Rowsell, McLean & Hamilton, 2012).
Overt Instruction & Guided Practice
Through the teacher instruction and their guided practice, the students will then be more sensitive to the design choices and the intentions behind the choices within the genre of Advertisements. The explicit teaching of the metalanguage facilitates classroom talk, which is a practice stemming from the Systemic Functional Approach that the Learning by Design Framework takes inspiration from (Lim, 2018).

Appendix 5:
Coraline Movie Poster
Appendix 6:
Analysis of the Visual and Textual Features


Appendix 7:
Guided Practice Resources



Lesson Development II
(10mins)
Resources needed:
-
Appendix 1
-
Google document
description
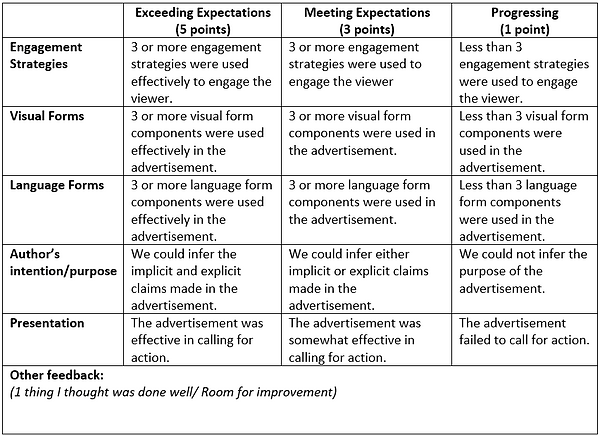
At this stage, the students will be creating their own rubrics for reviewing Print Advertisements.
-
In their groups, the students will create their own rubrics for peer assessments of Print Advertisements. Students should include the Visual and Language features (Appendix 1), as well as the engagement strategies as part of the assessment criteria.
-
Teacher will walk around and facilitate the creation of the rubrics.
rationale
As they co-create their rubrics, they are making explicit their understanding of the visual and language forms of Print Advertisements and the engagement strategies employed in the visual mode. They are the specific features that the students feel are more pertinent towards achieving the purposes of their advertisements. It also encourages them to take ownership of their learning.
The creation of the rubrics also serves as scaffolding for their creation of artefacts in the next lesson, where they can use it as self-assessment before they upload their artefacts onto Padlet or structuring their feedback to their friends during the peer assessment.

Appendix 8:
Suggested Class Rubrics